RFID
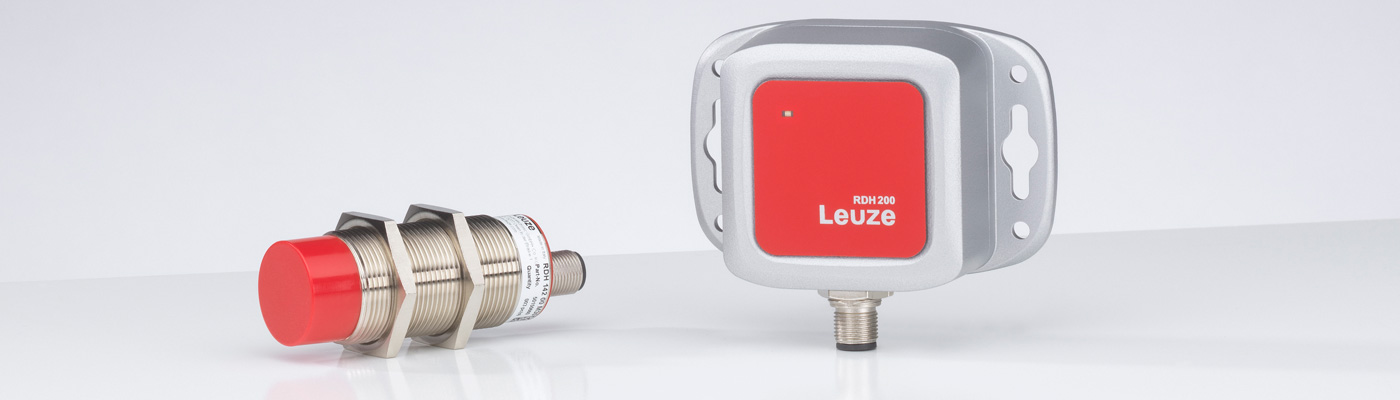


RFID, which stands for radio frequency identification, is a technology for identifying objects using electromagnetic fields and waves. An RFID system consists of at least one RFID transponder and one read/write unit, which have integrated and/or external antennae.
To transfer data between the transponder and the read/write unit or RFID reader, electromagnetic fields are used. The structure of each RFID transponder consists of an antenna and a microchip. A unique, unchangeable serial number, the unique ID (UID), is always stored on the microchip. Depending on the type of transponder and the technology used, further data storage for user-specific object data is available on the microchip.

RFID transponders can be active, meaning that they use an integrated power source for data transmission, or passive, meaning that they draw the energy required for data transmission from the RFID reader’s electromagnetic field. RFID systems use low frequencies/LF (125 kHz), high frequencies/HF (13.56 MHz) or ultra-high frequencies/UHF (865 MHz to 928 MHz) for data transmission. The frequencies used differ in terms of operating range, transmission rate and physical interactions in the environment.